Introduction |
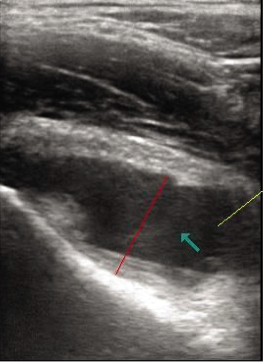
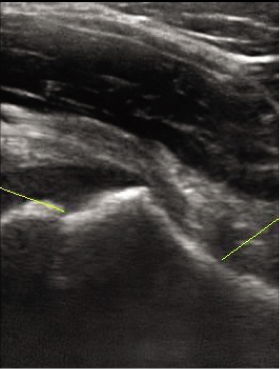
Hip septic arthritis is a surgical emergency. Prompt diagnosis and drainage are essential to prevent joint damage. In infants, septic arthritis may occur from propagation of adjacent osteomyelitis. Causative organisms include Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pneumoniae. Pain is typically acute, localized, and severe (refuses to bear weight) and accompanied by fever. Although occasionally the presentation is more subtle or afebrile. Bilateral effusions suggest a systemic arthritic disorder or transient synovitis.
|
Guidelines |
Guidelines for US-guided Hip Arthrocentesis
Kocher 4 criteria for child with painful hip:
|
Indications |
For Urgent Hip Arthrocentesis
Management approach
Diagnosis of septic arthritis
|
Contraindication |
Pre-Procedure |
Labs |
Synovial fluid
Blood
|
Technique |
Pathologic changes in synovial fluid
Other tests
|
Complications |
Follow-up |
References |
|